Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
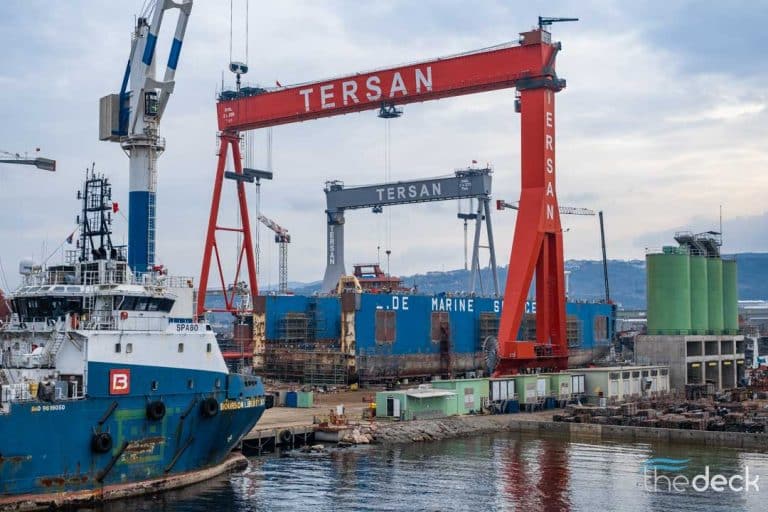

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
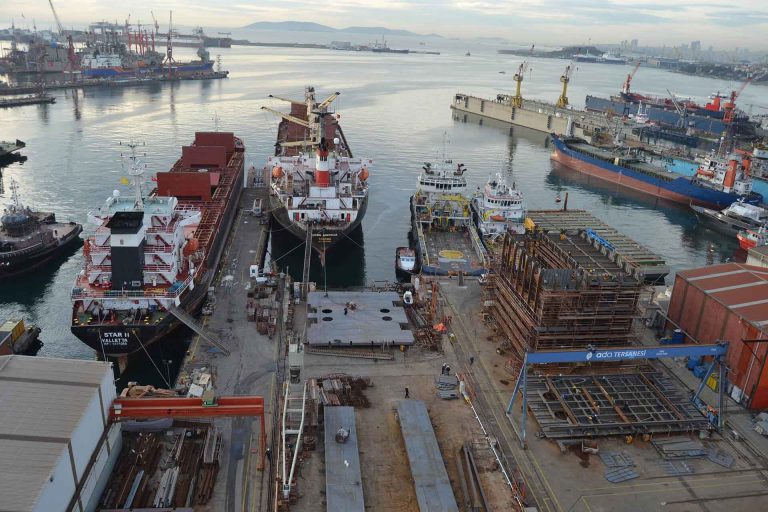

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
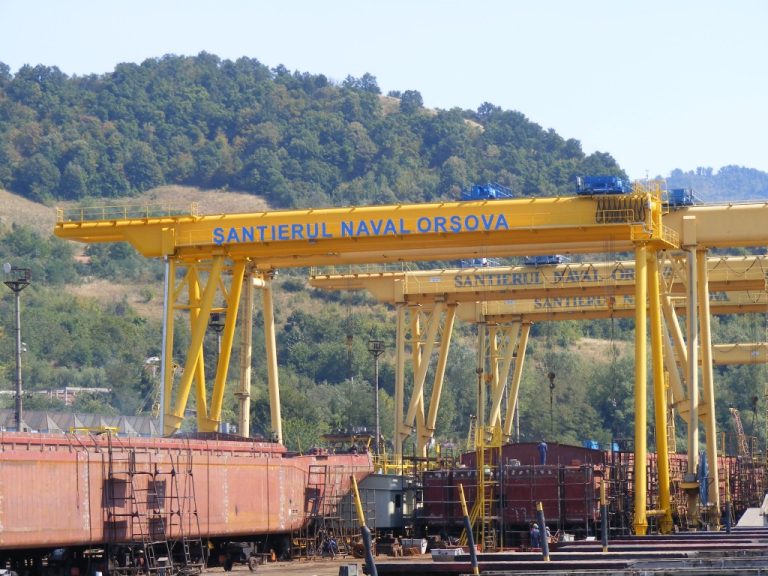

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, welding robot programming has emerged as a critical skill that bridges the gap between manual labor and advanced automation. According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global stock of industrial robots has surpassed 3 million units, with a significant portion dedicated to welding applications, which alone accounts for approximately 30% of all robotic deployments in industrial settings. As businesses strive for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness, mastering the intricacies of welding robot programming becomes essential not only for beginners but also for seasoned experts seeking to refine their techniques. Understanding the nuances of this programming is paramount, as it directly impacts production quality and operational reliability. With these insights, this guide provides invaluable tips and tricks to navigate the complexities of welding robot programming, ensuring practitioners at all levels can optimize their robotic systems successfully.

Welding robot programming is a critical skill in today’s automated manufacturing environment, catering to both beginners and seasoned professionals. Understanding the fundamentals of this technology is essential for anyone looking to enhance their programming skills. The basics involve familiarizing oneself with the robot’s interface, grasping the principles of motion control, and knowing the different types of welding processes used in the industry.
To ease into welding robot programming, beginners should start with simple tasks. One effective tip is to practice with simulation software before moving to actual robot operation. This allows learners to understand various commands and sequences without the risk of damaging equipment. Additionally, engaging with user manuals and community forums can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting techniques that simplify the learning process.
As programmers gain confidence, they can explore more complex projects by experimenting with different welding techniques, adjusting parameters, and optimizing paths for efficiency. A crucial tip for both beginners and experts is to continuously refine and document their programming processes. This practice not only helps in maintaining consistency but also serves as a reference for future projects, promoting ongoing improvement and mastery in welding robot programming.
Setting up a welding robot for optimal performance is crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in production. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global market for industrial robots is expected to grow by 12% annually, underscoring the importance of mastering robotic welding technologies. Proper setup not only enhances the robot's operational capabilities but also prolongs its service life.
Tip 1: Ensure Proper Calibration. It's essential to calibrate your welding robot accurately. A study from the American Welding Society highlights that improper calibration can lead to misalignment, which may result in a 20% reduction in welding quality. Regular calibration checks can help maintain precision, ensuring that the robot performs within the desired specifications.
Tip 2: Optimize Welding Parameters. Each material has unique welding requirements; therefore, adjusting the welding speed, voltage, and wire feed rate can significantly impact the quality of the weld. Data from a recent industry analysis indicates that optimizing these parameters can improve efficiency by up to 30%. Experimenting with different settings is essential to find the best combination for your specific application.

When programming welding robots, beginners and seasoned professionals alike can fall into common pitfalls that hinder their efficiency and output quality. One significant mistake is neglecting to thoroughly understand the robot's mechanics and the welding process. Without a grasp of how the robot operates and the specific requirements of the welding task, programmers may struggle to optimize settings, leading to issues such as poor weld quality or increased wear and tear on the equipment.
Another frequent error is failing to properly simulate the welding process before executing it in the real world. Rushing into actual welding without comprehensive simulations can result in costly misalignments and rework. Utilizing simulation software allows for identifying and troubleshooting potential problems beforehand, significantly reducing downtime. Additionally, overlooking the importance of consistent programming practices can complicate maintenance and future programming efforts. Adopting a standardized approach ensures easier collaboration and knowledge transfer among team members, enhancing overall productivity.
The welding robot market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advances in technology and an increasing demand for automation across various industries. According to recent reports, the robotic welding market is projected to continue expanding as manufacturers strive to improve productivity while addressing skilled labor shortages. Notably, welding robots and collaborative robots (cobots) are at the forefront, with organizations leveraging their capabilities to enhance operational efficiency. For instance, industries such as automotive and heavy manufacturing are increasingly adopting robotic solutions to streamline welding operations and achieve consistent quality in complex environments.
In the realm of welding robot programming, experienced programmers are discovering innovative techniques that enhance productivity and reduce production time. By utilizing advanced simulation software, programmers can optimize welding paths and anticipate potential issues before actual operations commence. This approach has led to substantial increases in output; one case study revealed a remarkable 50% rise in productivity attributed to effective offline programming strategies. As the industry embraces these cutting-edge practices, experienced specialists continue to refine their skills, ensuring that automated welding solutions remain integral to modern manufacturing processes.
When operating welding robots, troubleshooting common issues is essential to maintaining efficiency and preventing costly downtime. One prevalent problem is inaccurate weld bead placement, which can stem from misalignment between the robot and the workpiece. To address this, operators should regularly calibrate the robot’s position and verify that fixtures are secure and aligned correctly before starting a welding cycle.

Another frequent issue involves inconsistent weld quality, often resulting from fluctuations in the welding parameters. To resolve this, it is crucial to monitor the robot’s settings, such as voltage, amperage, and travel speed, ensuring they match the specifications for the material being welded. Additionally, failing to account for variations in material thickness can lead to poor weld penetration. Regular maintenance checks on the welding equipment and timely replacement of worn components can further enhance performance reliability and prolong the lifespan of the robot system.