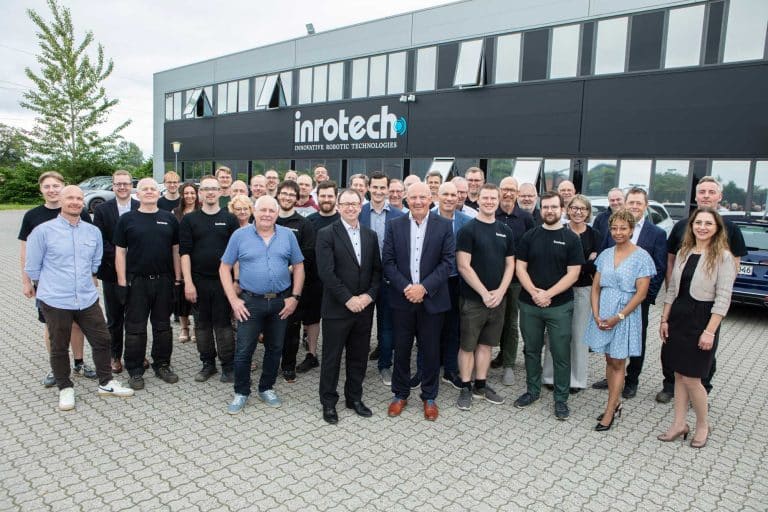

Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
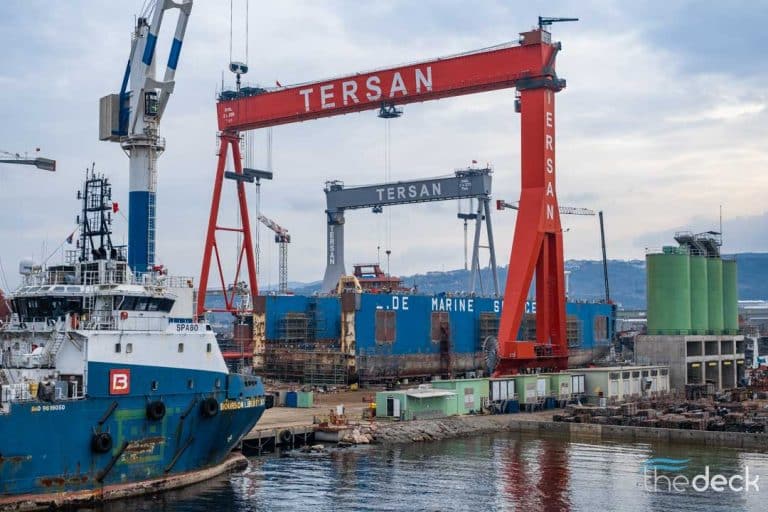

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
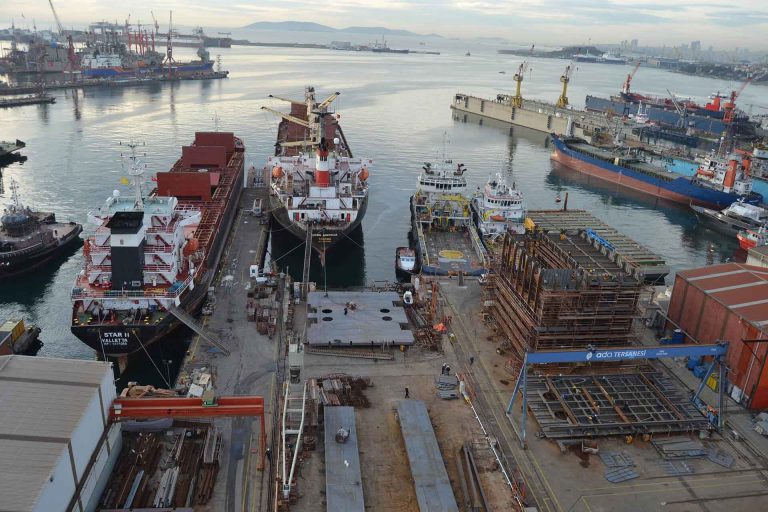

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
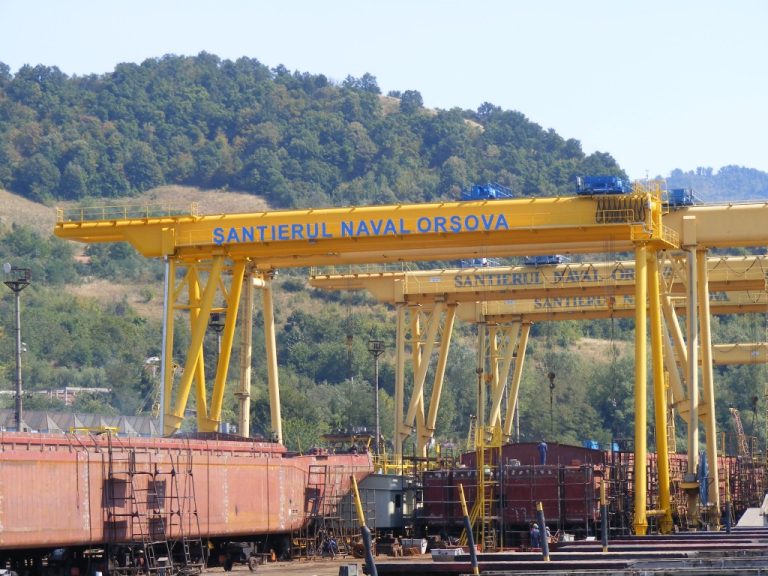

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
TIG robotic welding is gaining traction in various manufacturing sectors. This advanced technique uses tungsten inert gas for precision welding. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the global TIG welding market is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for automated solutions in welding applications.
Expert Mark Johnson, a leading figure in welding technology, states, “TIG robotic welding enhances quality and productivity.” The automation provided by robotics allows for consistent welds with minimal human intervention. However, challenges remain. The upfront cost of TIG robotic welding systems can be a barrier for small businesses. Not all materials are suited for TIG processes, limiting its application scope.
This technology might not be the solution for every welding need. It requires skilled operators for setup and maintenance. As the industry evolves, continuous innovation will be essential. Companies must weigh the benefits against potential limitations. The journey of TIG robotic welding is just beginning, with much to explore.
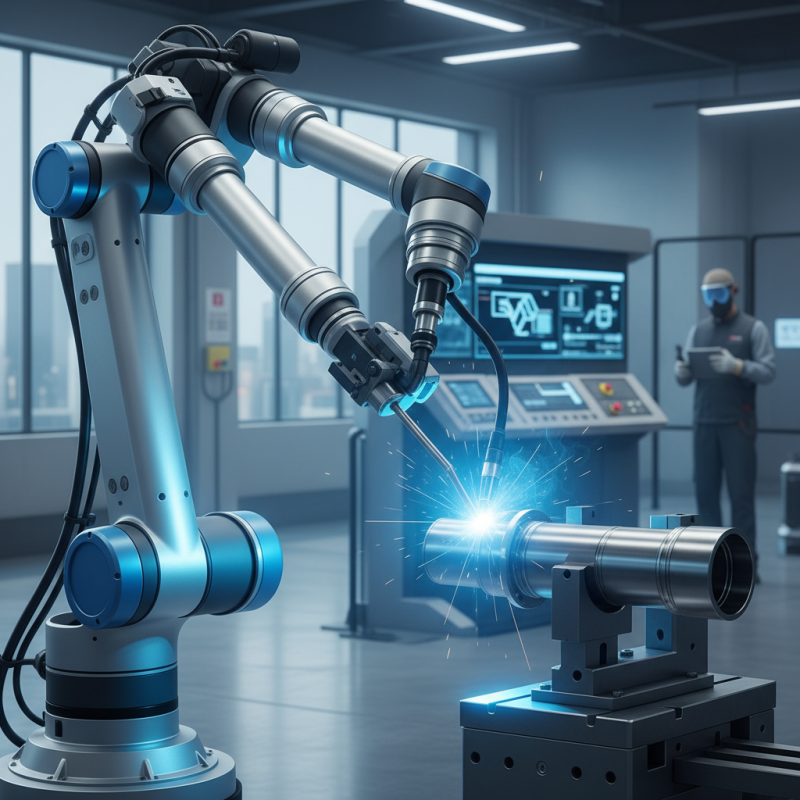

TIG robotic welding is a precise method used in various industries. It stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. This technique uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create a weld. Argon or other inert gases protect the weld area from contamination. As a result, the welds produced are cleaner and of higher quality.
One key aspect of TIG robotic welding is its versatility. It can be used on different materials, including stainless steel and aluminum. The process allows for thin sections to be welded without burning through. However, setting it up can be complex. Proper adjustments are necessary to ensure the right heat and gas flow.
Tips: Always clean the base materials thoroughly before welding. Impurities can lead to weak welds. Also, calibration of the robotic arm should not be overlooked. Improper calibration may cause failure in the welding process. Keep in mind that practice is essential. Each setup might require fine-tuning. Don’t be discouraged by failures; they can provide valuable lessons.
Tig robotic welding is a precise method used in various industries. Its key components ensure efficiency and quality in welds. The tungsten electrode plays a crucial role. It creates an arc between the electrode and the workpieces. This process requires a steady hand and keen eye. Any slight deviation can lead to defects.
Another essential component is the welding power supply. It provides the necessary current for welding. The type of power supply can affect the heat input. A mismatch may result in poor weld quality. Gas flow monitors are vital too. They ensure that the shielding gas flows correctly. Without proper shielding, oxidation can occur, compromising the weld.
The robot itself is a significant component. It must be programmed accurately for optimal results. A small error in programming can lead to misalignment. This can waste materials and time. Regular maintenance of robots is necessary. Wear and tear can affect precision, leading to issues in the welding process. Acknowledging these potential flaws is vital for continuous improvement.
TIG robotic welding is a precise and efficient process. It uses a tungsten electrode to produce an arc for welding. The robot arm holds the electrode and moves it along the joint. This ensures a uniform and clean weld. The process requires careful programming. Often, the angles and speed need adjustments based on the materials used.
The welding process involves several key steps. First, the workpieces are securely positioned. Clamping them correctly is crucial. Any misalignment can lead to poor weld quality. Next, the robot arm is programmed. It follows a designated path to ensure accuracy. The welding environment must be controlled, too. Disturbances, like wind or drafts, can affect the weld.
During the welding, continuous monitoring is necessary. Sensors check the temperature and the arc length. If something goes wrong, the robot needs to pause. It’s not uncommon for robots to make mistakes initially. Sometimes, welds can be inconsistent. Revisiting the parameters and practicing leads to improvement. This iterative process is essential for achieving success in TIG robotic welding.
Tig robotic welding presents notable advantages in industrial applications. One key benefit is precision. Robots can perform consistent welds, minimizing human error. This leads to better quality control across production lines. The speed of robotic systems also maximizes productivity. Processes that took hours can now be completed in minutes, significantly reducing labor costs.
Moreover, tig robotic welding enhances safety in the workplace. By automating hazardous tasks, it reduces the risk of injury to workers. Despite these benefits, challenges remain. Initial setup costs for robotic systems can be high. Training staff to operate and maintain these machines is essential but can be time-consuming. Companies must weigh these factors against potential gains.
Another advantage is the ability to work with various materials. Robotic systems can seamlessly weld aluminum, stainless steel, and more. This versatility expands manufacturing capabilities. However, relying solely on automation may hinder skill development in the workforce. Balancing technology with human expertise is crucial for sustainable industrial growth.
| Feature | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | TIG welding provides high precision and control over the welding arc. | Reduces defects and increases the quality of welds. |
| Versatility | Can be used on various materials including aluminum, stainless steel, and magnesium. | Suitable for a wide range of applications. |
| Automation | Robotic TIG welding automates the process for increased efficiency. | Increases productivity and reduces labor costs. |
| Control | Operators can easily adjust settings for different materials and thicknesses. | Enhances flexibility in manufacturing processes. |
| Safety | Reduces exposure to dangerous fumes and heat for workers. | Improves workplace safety standards. |
Robotic welding technology is experiencing significant growth. The market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This increase is driven by advancements in automation and manufacturing processes. Companies seek efficiency and precision, and robotic welding delivers both.
In 2021, the global robotic welding market was estimated to be worth billions. By 2028, it could surpass these numbers. Industries like automotive and aerospace are particularly focused on adopting this technology. They aim for higher productivity and reduced labor costs. However, challenges remain. Some manufacturers struggle with integration and training. The transition to automation can be costly and complex.
Nonetheless, trends show a rising interest in flexibility and adaptive systems. Many new robots feature enhanced programming capabilities. These improvements allow for easier adjustments during production. Moreover, industries are increasingly relying on data analytics. This practice aims to optimize the welding process. As the landscape evolves, businesses will need to address both the benefits and challenges of robotic welding technology.














