Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
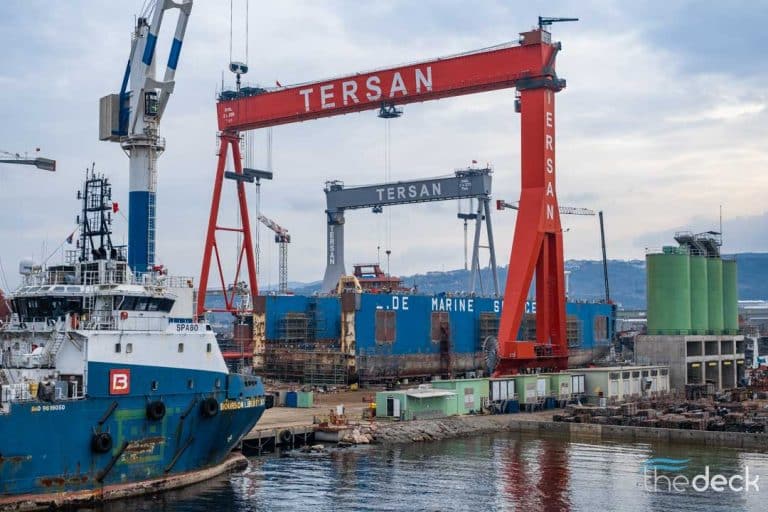

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
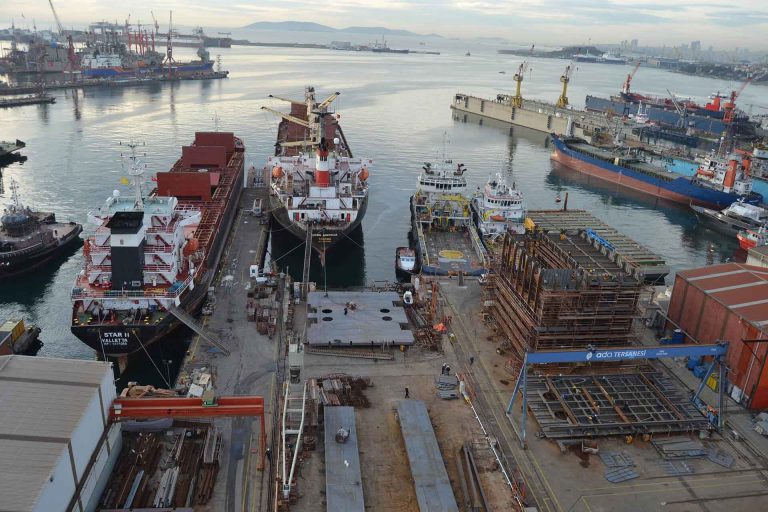

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
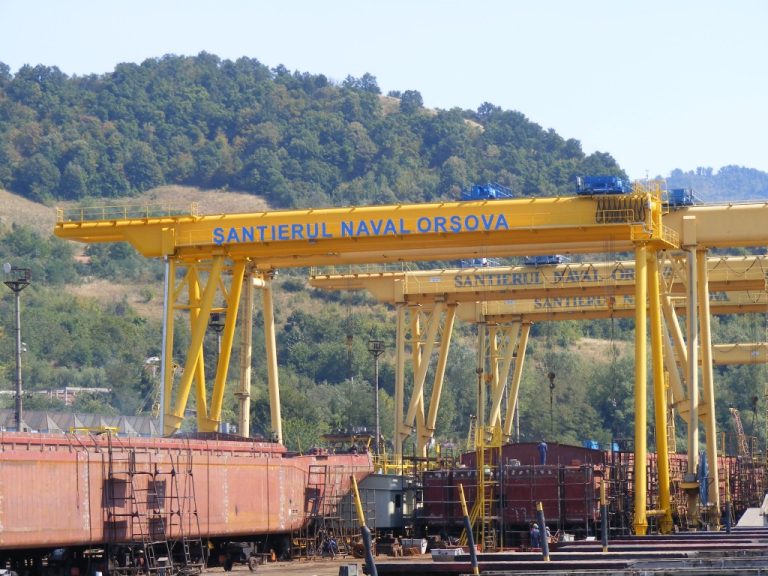

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
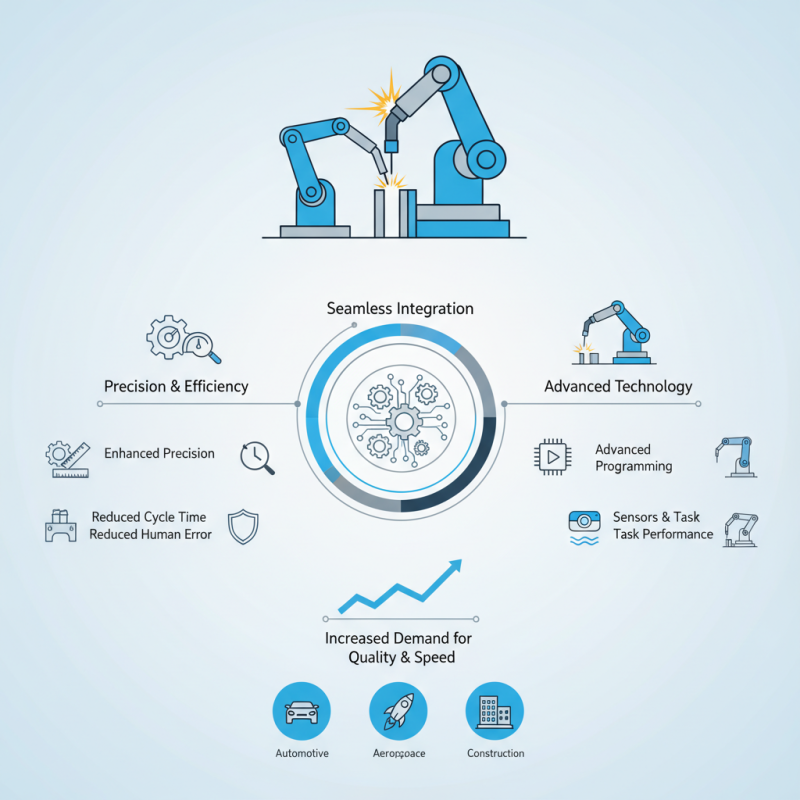
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing and automation, the robotic welding machine stands out as a revolutionary technology that is reshaping welding processes across various industries. This sophisticated equipment not only enhances precision and efficiency but also significantly reduces human error and labor costs. By harnessing advanced programming and robotic arms, these machines perform complex welding tasks with unparalleled consistency, making them indispensable in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The operation of a robotic welding machine involves a seamless integration of mechanical engineering and computer technology. These machines utilize sensors and software to analyze and respond to real-time conditions, ensuring optimal weld quality. As the demand for high-quality, rapid production increases, understanding the functionality and advantages of robotic welding machines becomes essential for manufacturers aiming to stay competitive in the global market. This introduction will delve into the intricacies of how robotic welding machines work and the significant benefits they offer to the modern manufacturing landscape.
A robotic welding machine is an advanced piece of equipment that utilizes automated processes to perform welding tasks with high precision and efficiency. These machines are typically programmed to execute specific welding techniques such as MIG, TIG, or spot welding, depending on the requirements of the task. By incorporating robotic arms equipped with welding tools, these machines can maneuver seamlessly, ensuring consistent weld quality across a variety of projects.
The operation of a robotic welding machine begins with a pre-programmed set of instructions that dictate the movement and actions of the welding robot. Sensors and advanced software guide the machine, allowing it to make real-time adjustments for optimal performance. The robotic arm can reach complex angles and positions that would be challenging for human welders, significantly increasing productivity while reducing the risk of errors and defects. Additionally, these machines can operate continuously, which enhances production rates and diminishes labor costs, making them an invaluable asset in modern manufacturing environments.
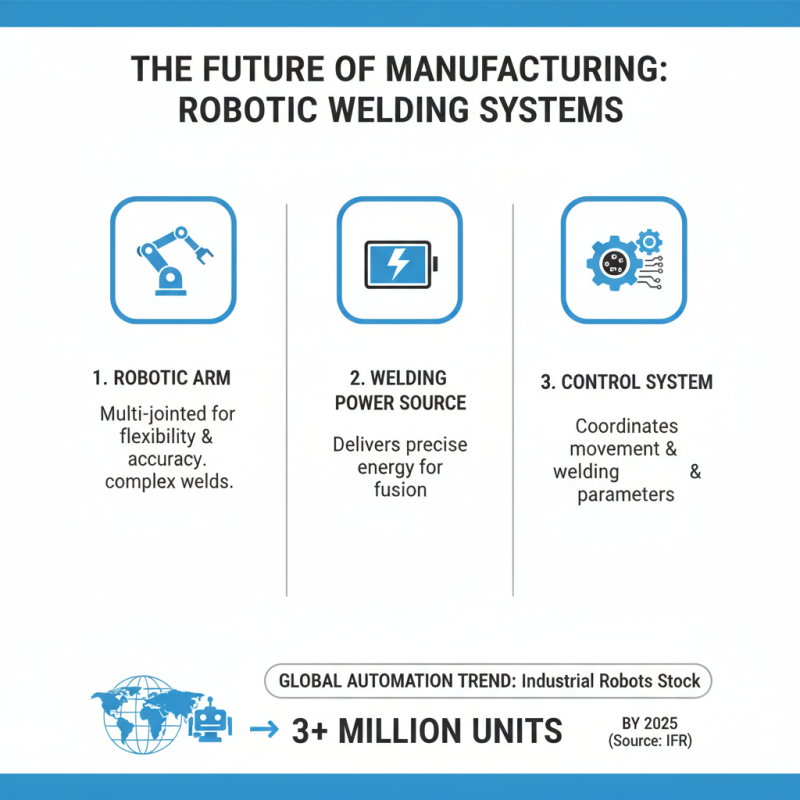
Robotic welding systems have become an integral part of modern manufacturing due to their precision and efficiency. The key components that make up these systems include the robotic arm, the welding power source, and the control system. The robotic arm, typically equipped with multiple joints, allows for flexibility and movement, enabling the machine to perform complex welding tasks with high accuracy. According to the International Federation of Robotics, the global stock of industrial robots is anticipated to surpass 3 million units by 2025, further underlining the growing trend towards automation in welding processes.
The welding power source varies depending on the welding technique used—whether MIG, TIG, or spot welding. Each method requires specific voltage and amperage settings to achieve optimal weld quality. Additionally, the control system plays a crucial role by coordinating the movements of the robotic arm and fine-tuning the welding parameters in real time. This integration enhances the repeatability of welds, significantly reducing variability that can occur in manual welding.
Tips: When considering the implementation of a robotic welding system, assess the compatibility of the robotic arm with your existing production line. Furthermore, investing in quality training for operators can maximize the benefits of automation, ensuring the system is used to its full potential. Remember, regular maintenance of components like the welding power source can prevent downtime and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Robotic welding machines have revolutionized the manufacturing sector with their precision and efficiency. These machines operate based on a set of programmed instructions that allow them to perform welding tasks autonomously. The core working principle involves a robotic arm equipped with a welding torch or electrode, which is programmed to follow a pre-defined path. Advanced sensors and cameras can also be integrated to fine-tune the welding process, providing real-time feedback and adjustments to ensure high-quality welds. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the robotic welding market is projected to reach USD 5.3 billion by 2025, driven by a rise in automation across various industries.
The welding process typically uses either Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) or Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding methods, where the robotic arm maneuvers precisely to join materials together at high temperatures. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in these machines enhances their capabilities, enabling them to adapt to different welding parameters and improve overall efficiency. A study from the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology indicated that robotic welding can increase production rates by as much as 20-30% while reducing the overall labor costs associated with welding operations. This capability not only streamlines manufacturing processes but also maintains consistent quality across products.
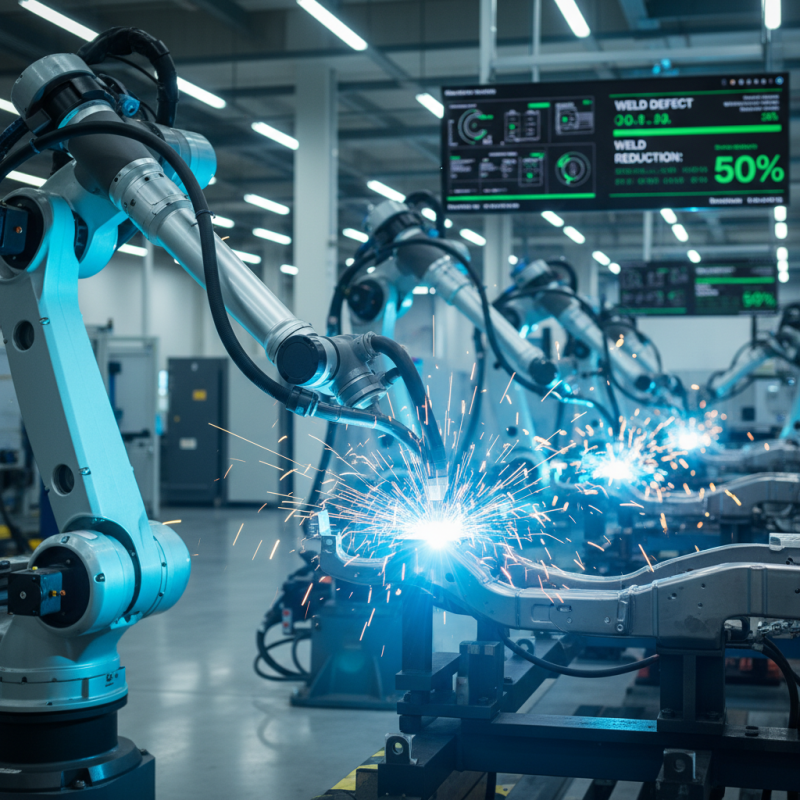

Robotic welding technology offers a myriad of advantages that have revolutionized the manufacturing sector. One of the most significant benefits is the enhancement of precision and quality in welding processes. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, industries utilizing robotic welding systems have seen a reduction in weld defects by as much as 50%. This precision is largely attributed to the machines' ability to perform consistent welds without the variability of human labor, ensuring a high standard of quality in production.
Moreover, robotic welding improves efficiency and reduces labor costs. A study from the Welding Institute indicates that companies that have integrated robotic systems into their welding processes reported productivity increases of up to 30%. This efficiency not only accelerates production cycles but also allows human workers to focus on more complex tasks, leading to a more skilled workforce. Furthermore, the implementation of robotic welding significantly minimizes workplace accidents associated with manual welding, contributing to a safer working environment, which is paramount in today's industrial landscape. Thus, the benefits of employing robotic welding technology extend beyond mere cost savings, influencing overall operational efficiency and workplace safety.
Robotic welding machines have become indispensable across various industries, revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape with their precision and efficiency. In the automotive sector, for instance, robotic welding is crucial for assembling vehicles, enabling manufacturers to achieve consistent weld quality while maximizing production speed. The machines handle complex tasks such as spot welding and seam welding, ensuring that critical components like body panels and frames are securely bonded together. This not only enhances the structural integrity of vehicles but also minimizes human error and the time required for production.
In the aerospace and construction industries, robotic welding plays a vital role in building components that demand exceptional quality and durability. Aerospace manufacturers utilize robotic systems to weld lightweight materials, including aluminum and composites, which are essential for aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. Similarly, in construction, robotic welding supports the production of sturdy metal structures and frameworks, ensuring that they meet stringent safety and quality standards. The versatility of robotic welding allows it to adapt to different materials and welding techniques, making it an ideal solution for various industrial applications.