Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
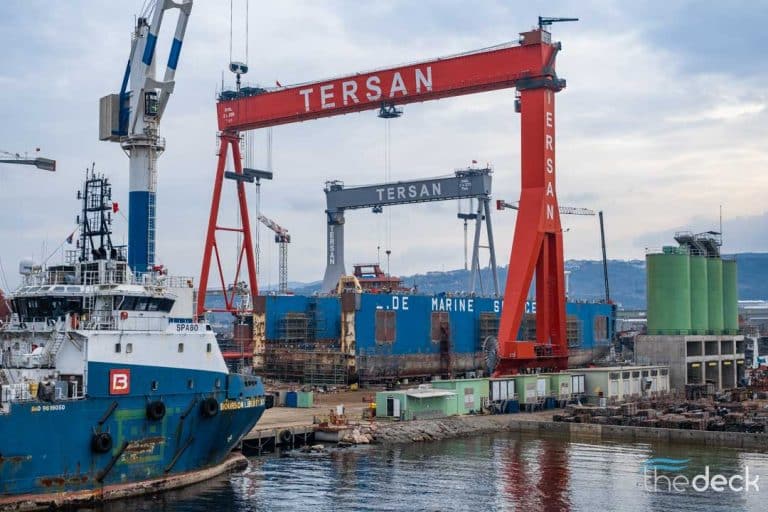

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
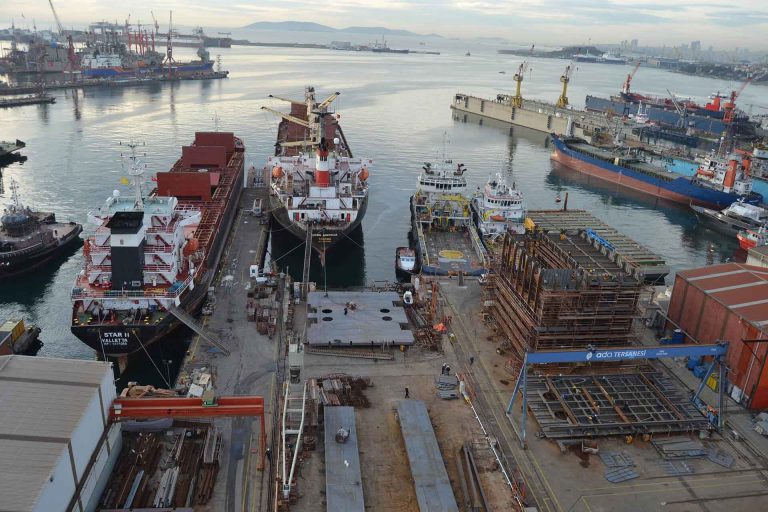

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
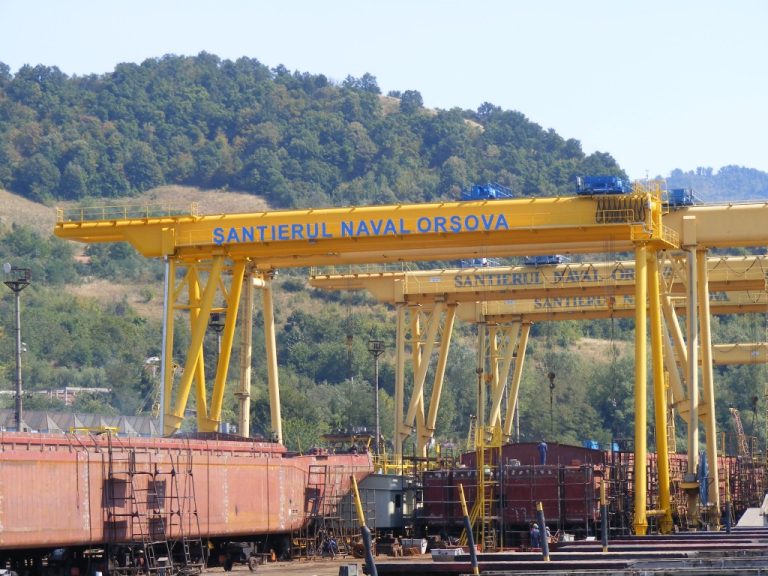

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the demand for skilled professionals in robotic welding jobs is growing significantly. With advancements in technology, companies are increasingly turning to automation for efficiency and precision in welding processes. As noted by renowned welding industry expert Dr. Steven Blake, "The integration of robotics in welding not only enhances productivity but also opens up exciting career opportunities for those willing to adapt to new technologies."
This shift in the industry creates a favorable environment for aspiring welders to explore the top ten robotic welding jobs available today. These positions not only promise lucrative salaries but also offer a chance to work with cutting-edge technology that is transforming traditional welding practices. As we delve into this comprehensive guide, we will uncover the various roles within the robotic welding sector, the skills required, and how to prepare for a successful career in this dynamic field. Embracing the future of welding means recognizing the vital role robotic welding jobs play in redefining the industry and paving the way for skilled professionals to thrive.
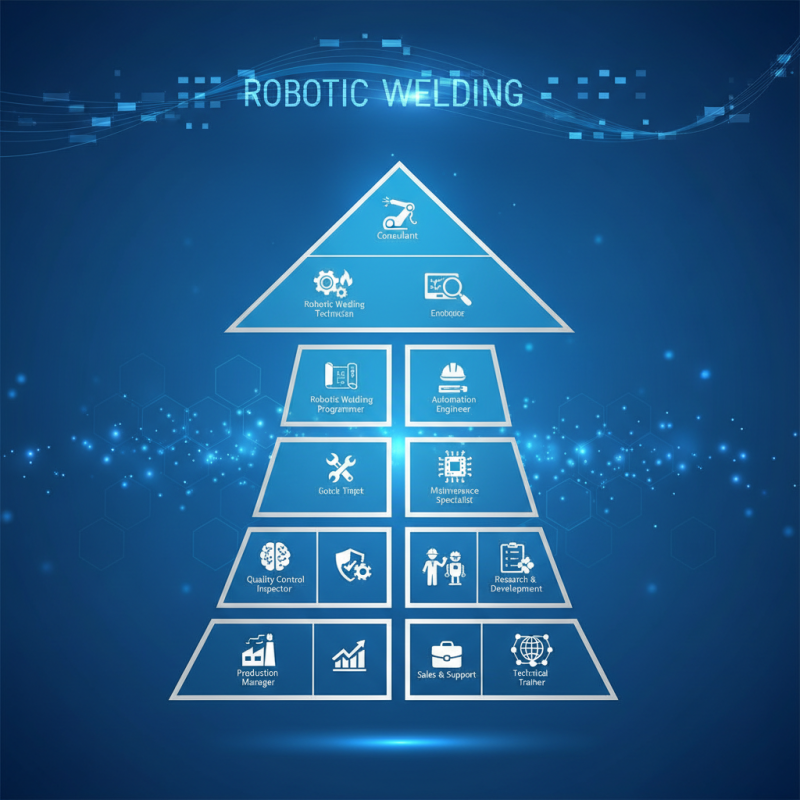
The field of robotic welding is experiencing rapid growth as industries increasingly adopt automation to enhance productivity and efficiency. In today’s job market, the demand for skilled professionals who can operate and maintain robotic welding systems is on the rise. This shift is driven by the need for precision and consistency in manufacturing processes, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors. As companies strive to remain competitive, they are actively seeking individuals who possess the technical know-how to harness the capabilities of robotic welding technology.
For those considering a career in robotic welding, numerous opportunities exist. Positions range from robotic welding operators who manage the machines on the shop floor to robotic programmers responsible for developing and fine-tuning automation processes. Additionally, technicians who specialize in the maintenance and troubleshooting of robotic welding systems are also in high demand. With the right training and certifications, individuals can position themselves for lucrative careers that not only offer competitive salaries but also the chance to work in cutting-edge environments. As the industry evolves, continuous learning and skill development will be essential for career advancement in this dynamic field.
In the rapidly evolving field of robotic welding, the demand for skilled professionals is on the rise, reflecting a significant shift towards automation in manufacturing processes. Recent industry reports indicate that the global market for robotic welding is projected to grow by over 9.3% annually through 2027, highlighting the urgency for workers equipped with the necessary skills. As companies increasingly adopt advanced technologies, candidates looking to establish a career in this sector must focus on developing a strong foundation in various essential skill areas.
A successful career in robotic welding necessitates a mix of technical knowledge and practical abilities. Proficiency in robotics programming languages, such as Python and C++, is crucial, as it allows operators to customize and control welding processes effectively. Additionally, understanding welding processes and techniques—such as MIG, TIG, or stick welding—is vital for troubleshooting and ensuring quality output. Data from the American Welding Society reveals that nearly 67% of employers prioritize hands-on experience combined with solid theoretical knowledge, underscoring the importance of vocational training and certification in this specialized domain. Furthermore, familiarity with computer-aided design (CAD) software is increasingly advantageous, as it aids in planning and optimizing welding operations.
Soft skills are equally important in robotic welding careers. Effective communication and teamwork are vital, as workers often collaborate with engineers and other technicians to troubleshoot and enhance robotic systems. Adaptability is another key trait, given the rapid technological advancements in this field. According to a recent study by the International Federation of Robotics, companies seeking to integrate robotic systems must prioritize training programs that enhance both hard and soft skills to fully harness the potential of automation in their operations. As the industry continues to expand, those who invest in their skill development will find themselves well-positioned for a lucrative career.
| Job Title | Average Salary (USD) | Required Skills | Education Level | Job Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Welding Technician | $50,000 | Programming, Mechanical Skills | Associate Degree | 7% |
| Robotics Engineer | $85,000 | Programming, Design, Problem Solving | Bachelor’s Degree | 9% |
| Manufacturing Engineer | $75,000 | CAD, Process Improvement | Bachelor’s Degree | 6% |
| Welding Supervisor | $70,000 | Leadership, Technical Knowledge | High School Diploma | 5% |
| Automation Technician | $60,000 | Troubleshooting, Technical Skills | Associate Degree | 8% |
| Robotics Technician | $55,000 | Installation, Maintenance | Associate Degree | 7% |
| Quality Control Inspector | $50,000 | Attention to Detail, Inspection Skills | High School Diploma | 4% |
| Research and Development Engineer | $90,000 | Analytical Skills, Innovation | Master’s Degree | 10% |
| Field Service Engineer | $68,000 | Customer Service, Technical Skills | Bachelor’s Degree | 6% |
| System Integrator | $80,000 | Systems Design, Problem Solving | Bachelor’s Degree | 7% |
In today’s manufacturing landscape, robotic welding is becoming increasingly essential across various industries due to its efficiency and precision. The automotive sector stands out as the primary employer for robotic welding professionals, with the demand for high-volume production and complex assembly processes that require automation. Companies in this industry rely on robotics to enhance production rates while maintaining consistent quality and safety standards.
Beyond automotive, the aerospace sector is also actively seeking skilled robotic welders to streamline the fabrication of components and improve the structural integrity of aircraft. The need for lightweight and durable materials in aerospace design has led to a greater reliance on advanced welding techniques, framed by automation. Additionally, sectors like construction and metal fabrication are employing robotic welding to improve operational efficiency and reduce labor costs, continuing the trend toward automation in various applications. Together, these industries present a wealth of opportunity for prospective robotic welding professionals looking to forge a rewarding career path.
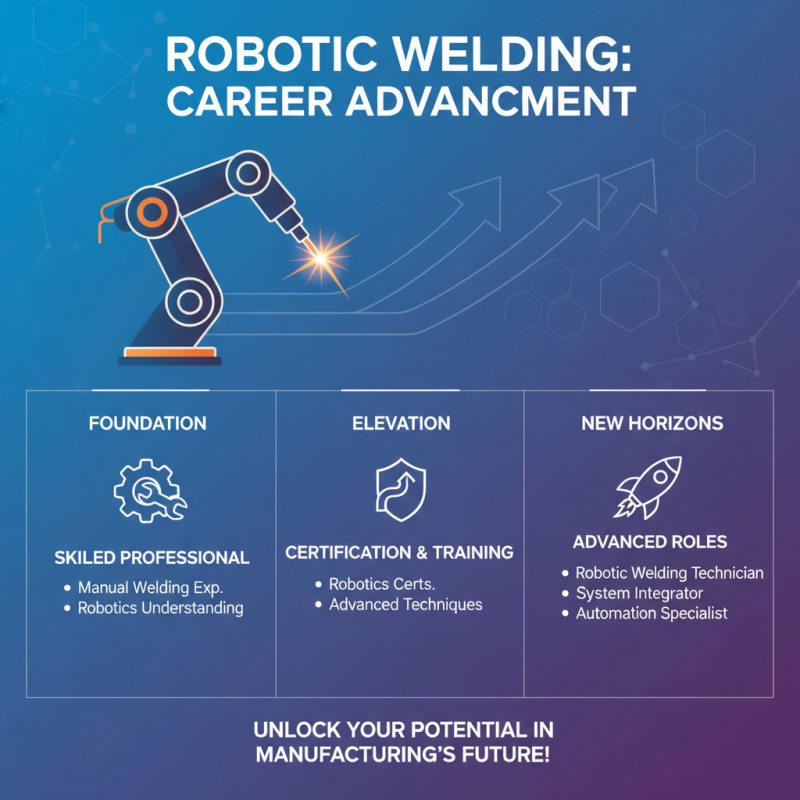
Robotic welding is rapidly transforming the manufacturing landscape, presenting numerous career advancement opportunities for skilled professionals. As industries increasingly adopt automation to enhance productivity and precision, individuals proficient in robotic welding can find themselves at the forefront of this technological revolution. With a robust understanding of robotics and welding techniques, workers can elevate their qualifications through certification programs and specialized training, opening doors to advanced roles such as robotic welding technician or system integrator.
Moreover, the demand for robotic welding expertise is expected to grow, with job roles evolving to encompass more than just operation. Professionals can pursue careers in programming, system maintenance, and even project management within automation projects. As companies seek to improve efficiency and reduce costs, the ability to troubleshoot, maintain, and optimize robotic systems will become increasingly valuable. Networking within the industry and gaining experience with various robotic systems can further enhance one's career trajectory, leading to positions in consultancy and leadership roles that influence the strategic direction of manufacturing processes.
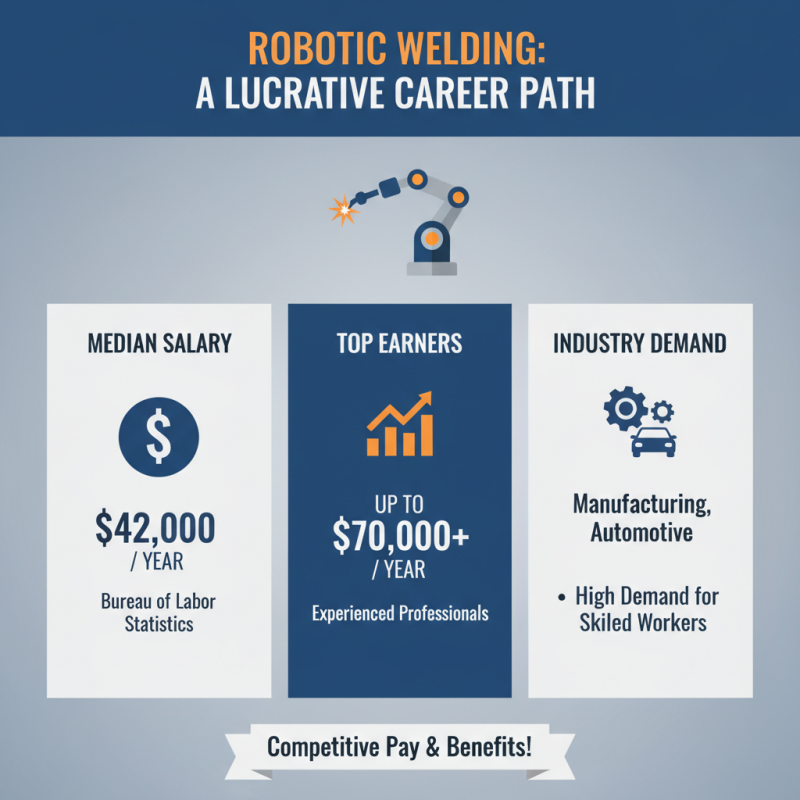
The field of robotic welding offers a promising career path with competitive salary expectations and enticing job benefits. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median salary for welders, including those specializing in robotic welding, is approximately $42,000 per year. However, experienced robotic welders can command significantly higher wages, with top professionals earning upwards of $70,000 annually. This lucrative compensation reflects the high demand for skilled workers in industries such as manufacturing and automotive, where robotic welding plays a critical role in maintaining productivity and precision.
In addition to a solid salary, robotic welders enjoy various job benefits that enhance their overall career satisfaction. Many employers provide opportunities for ongoing education and training, which not only help workers hone their skills but also pave the way for advancement into supervisory or specialist roles. Benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid vacations are common in this field, contributing to a stable and rewarding work environment. As automation continues to rise, the demand for robotic welders is projected to grow, making this an exciting time to enter the profession and take advantage of its many rewards.