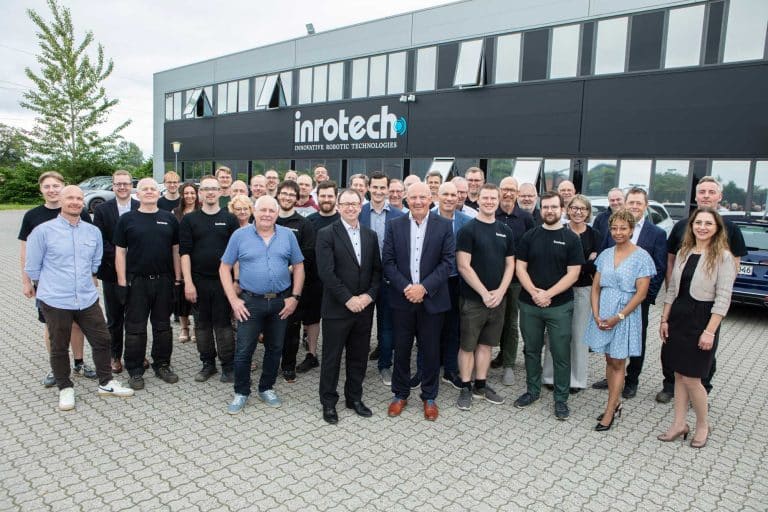
Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
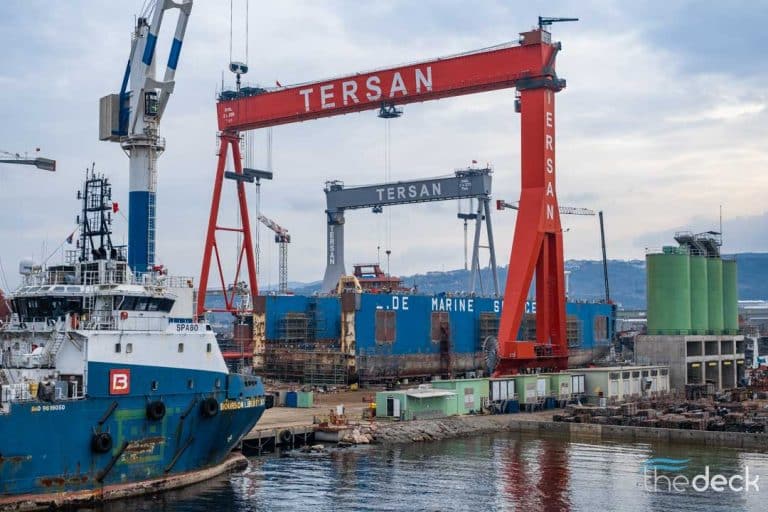

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
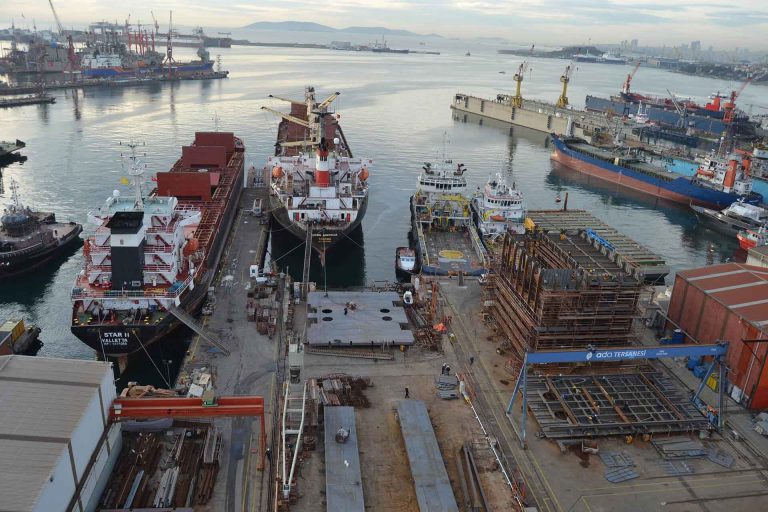

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
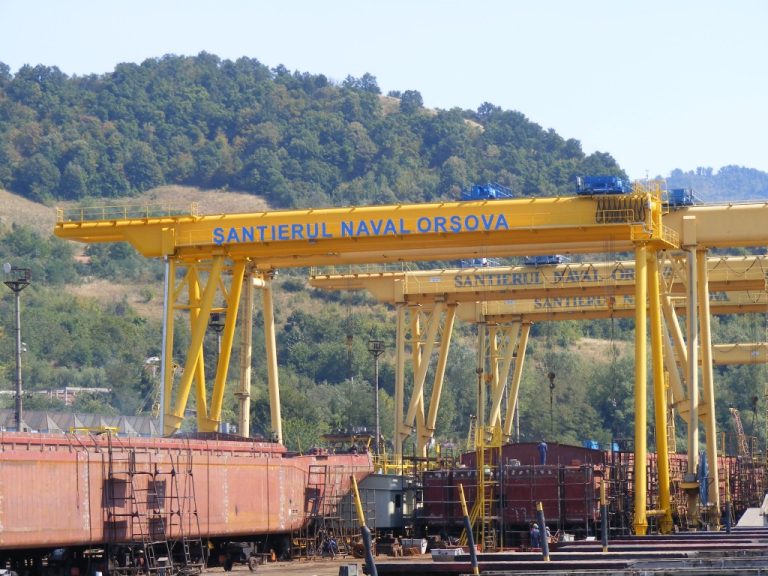

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
In 2026, the adoption of robotic welding systems is poised to revolutionize manufacturing processes. Industry reports indicate a 15% growth in the robotic welding market over the next few years. This shift is driven by the demands for precision and efficiency. Leading experts, like Dr. Emily Carter from the Robotics Institute, emphasize, "Automation is no longer an option; it’s a necessity for competitive production."
Robotic welding systems enhance productivity and consistency. However, the transition requires careful planning and training. Companies may struggle with the initial investment and the learning curve. A recent survey shows that 40% of manufacturers hesitate to adopt robotic systems due to these challenges. Finding skilled operators remains a challenge, with many organizations facing a talent gap.
Yet, the potential benefits are immense. Robotic welding reduces errors and increases throughput. As noted, "Businesses embracing this technology see significant improvements." As we look toward 2026, the landscape of manufacturing will undoubtedly shift. Embracing robotic welding systems may be daunting, but the rewards could redefine operational success.

In 2026, robotic welding systems are becoming essential in manufacturing. Factories are increasingly adopting automation to enhance precision and productivity. However, the transition is not without challenges. Some systems may struggle with complex geometries. Workers need training for effective collaboration with these robots.
The efficiency of robotic welding often depends on the programming and setup. Inaccurate calibration can lead to defective welds, impacting production quality. Additionally, integration with existing processes can be difficult. Companies must assess their unique needs before investing. Dedicating enough time for testing is crucial.
Despite these hurdles, the benefits of robotic welding are significant. These systems can operate continuously, reducing labor costs. With proper implementation, they can enhance production rates. Still, businesses must remain vigilant. Regular maintenance and updates are essential to keep systems functioning optimally.
When considering robotic welding systems, efficiency is paramount. Key features significantly impact productivity. An efficient system should offer speed, accuracy, and adaptability. Research shows that over 70% of industrial manufacturers are investing in robotic welding to increase output and reduce labor costs.
Integration of advanced sensors enhances precision. These sensors allow for real-time adjustments. This adaptability minimizes errors and improves weld quality. Additionally, systems with predictive maintenance can alert operators to potential failures. This feature reduces downtime by 30%, proving essential for high-volume production environments.
Training and software usability are often overlooked. A user-friendly interface decreases the learning curve for operators. However, many companies still face challenges in integrating these systems into existing workflows. Transitioning might require substantial changes in personnel training and equipment. These hurdles remind us that efficiency is not just about machines; it also involves human factors.
Robotic welding technology is evolving rapidly. Many top manufacturers are at the forefront, pushing innovation. These producers focus on efficiency and precision. Their systems have transformed manufacturing processes, enhancing production speed. Users can see significant reductions in cycle times when employing these advanced systems.
Yet, not all robotic solutions fit every industry. Some companies struggle with integration. Issues often arise during initial implementation stages. Proper training and familiarization are crucial for smooth operation. Potential users should assess their specific needs before committing to a system. Experimentation and feedback can reveal hidden challenges in daily use.
Advanced robotic welding systems come with a steep learning curve. Maintenance and adjustments might be necessary over time. Technicians must be well-trained to ensure optimal performance. Evaluating manufacturers based on support capabilities is vital. A strong partnership can lead to remarkable improvements in efficiency.
Robotic welding systems are making waves across various industries. These systems increase efficiency and reduce human error. In manufacturing, the automotive sector leads the way, using robotic welders for precise assembly. Reports indicate that about 70% of automotive welding tasks are automated. However, the implementation can be expensive and requires skilled operators for maintenance.
In construction, robotic welding is gaining traction as well. According to industry studies, around 30% of construction projects now incorporate welding automation to speed up processes. Despite this progress, many companies still face challenges. Training staff to operate and troubleshoot robots effectively is crucial but often overlooked.
As the demand for high-quality welds grows, companies must adapt. Some industries struggle with productivity due to outdated methods. Integration of robotic systems requires a cultural shift. Organizations must embrace technology while addressing employee concerns about job security. With proper planning, the benefits can outweigh these hurdles, leading to a more efficient workforce.
| Welding System | Industry Application | Welding Type | Production Efficiency (%) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System A | Automotive Manufacturing | MIG Welding | 95 | High-speed operation, precision control |
| System B | Aerospace | TIG Welding | 92 | Excellent weld quality, lightweight design |
| System C | Construction Equipment | Submerged Arc Welding | 90 | Deep penetration, robust frameworks |
| System D | Shipbuilding | Flux-Cored Arc Welding | 93 | Supports thick materials, anti-spatter technology |
| System E | Metal Fabrication | Plasma Welding | 94 | Versatile for various metals, minimal thermal distortion |
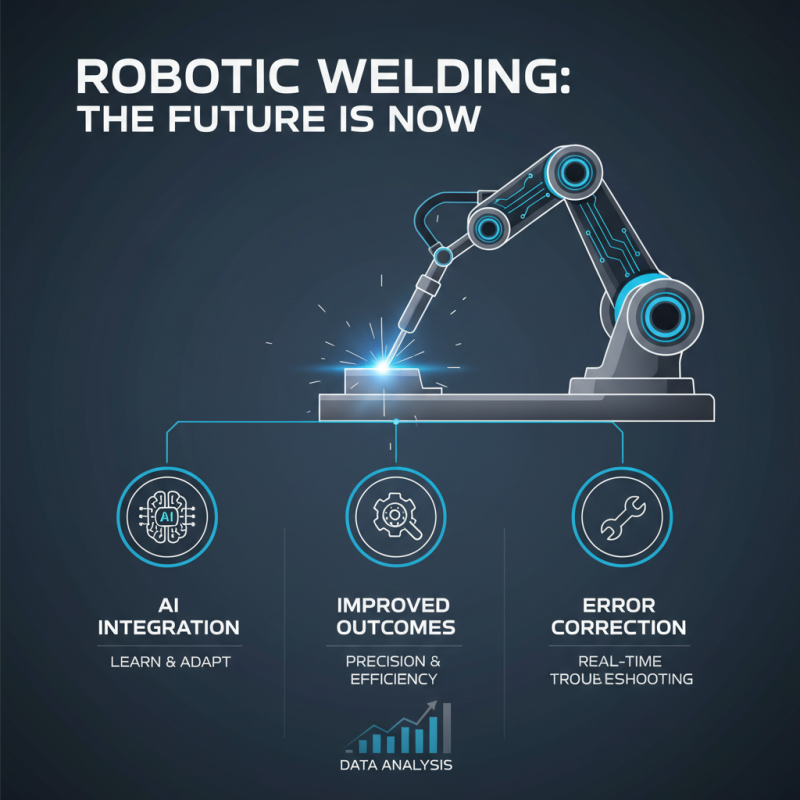
The future of robotic welding systems is undeniably exciting. Innovations are rapidly transforming the industry. One notable trend is the integration of artificial intelligence. This allows robots to learn and adapt to various welding tasks. Precision and efficiency improve as robots analyze data in real time. The ability to troubleshoot errors is a game-changer.
Another trend is the development of collaborative robots. These robots work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity. They can handle repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex work. However, challenges remain. Not all robots can seamlessly coexist with human workers. Safety concerns need addressing. Also, the adaptability of robots to different welding materials can be an issue. Industries must consider these factors carefully.
Advanced sensor technologies are also shaping the future. These sensors provide immediate feedback, ensuring quality control. While this technology is promising, it lacks universal standards. Inconsistent implementation can lead to issues. The best robotic welding systems will be those that balance innovation and practicality. Exploring these trends will guide manufacturers in making informed choices.