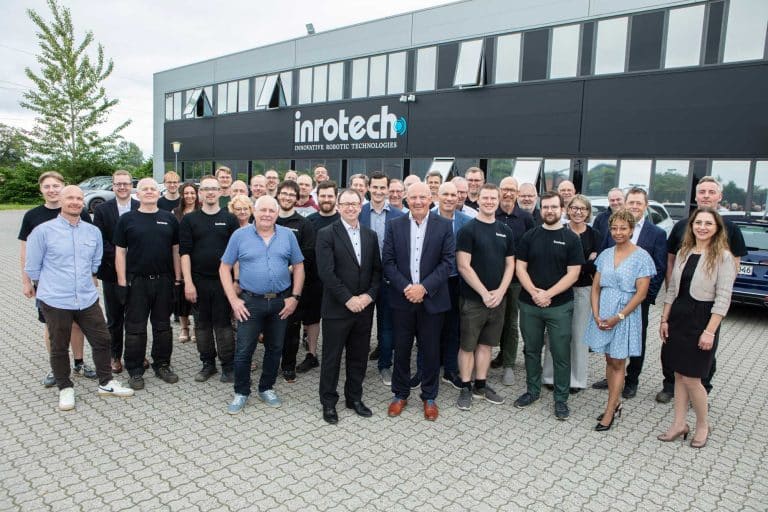

Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
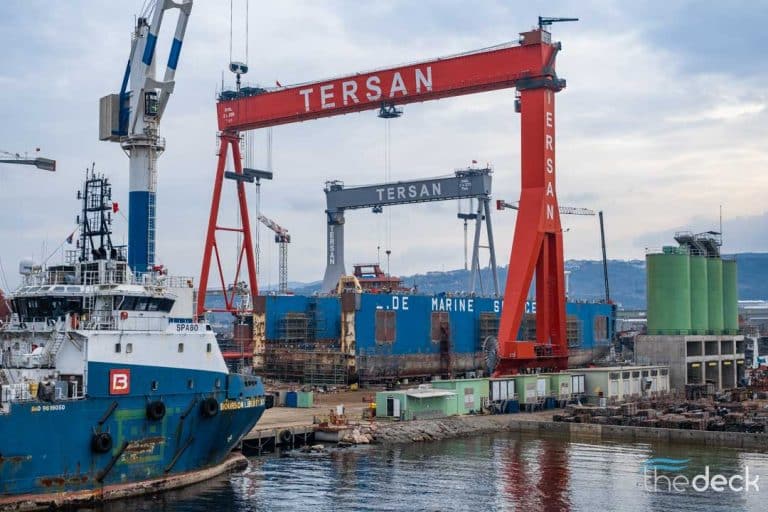

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
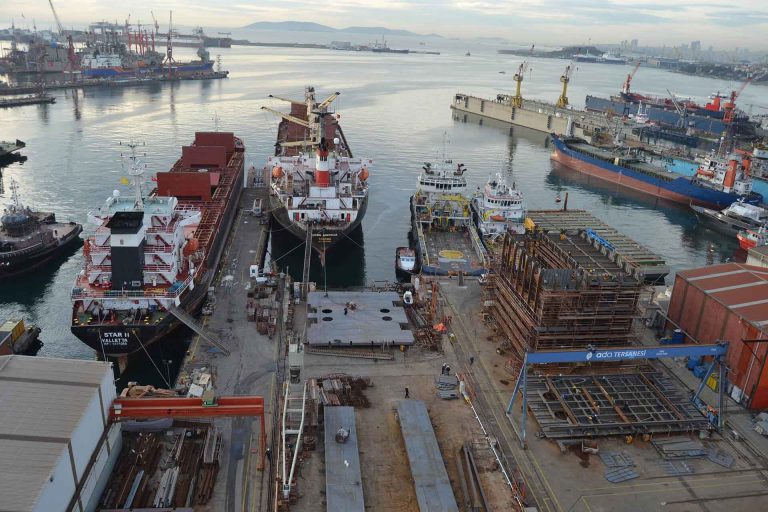

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
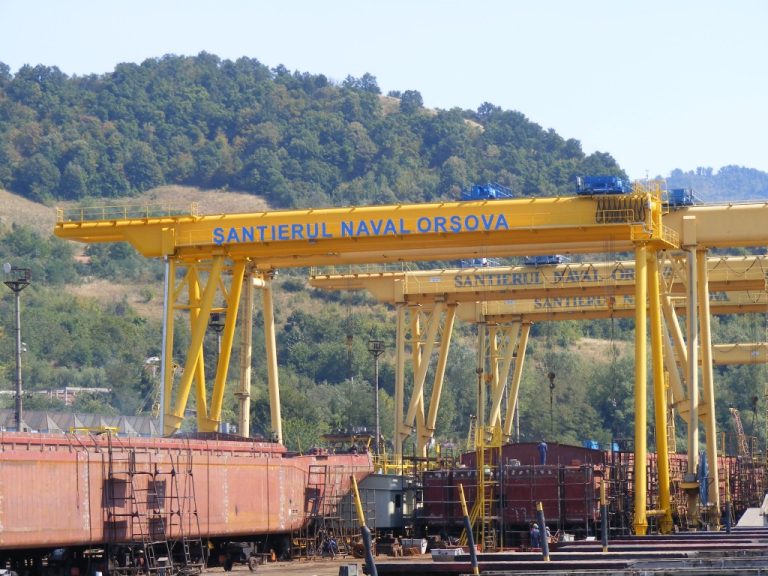

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the demand for skilled professionals in robotic welding has never been greater. Companies are increasingly turning to automation to enhance efficiency and precision in their welding processes. As a result, investing in robotic welding classes has become crucial for those looking to advance their careers in this field. Industry expert Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned figure in robotic manufacturing education, emphasizes, “Continuing education in robotic welding is essential; it not only enhances technical skills but also opens doors to innovative career paths.”
These classes serve as a vital stepping stone for aspiring welders and seasoned professionals alike, providing them with the knowledge and hands-on experience needed to operate and program advanced robotic systems. With a curriculum designed to cover the latest technologies and methodologies, participants can expect to gain insights that will keep them competitive in the job market. By enrolling in robotic welding classes, individuals can not only boost their technical competencies but also position themselves for leadership opportunities in a field that is constantly evolving.
As the industry continues to expand, so do the prospects for those equipped with robust robotic welding skills. The future belongs to those who embrace this technological shift and seek out education that allows them to thrive. Investing in robotic welding classes is not merely an enhancement of skills; it is a strategic move towards securing a successful and fulfilling career in the world of advanced manufacturing.
Robotic welding has become a critical component of modern manufacturing, significantly enhancing productivity and precision in various industries. The global market for industrial robotics is projected to grow from $87.1 billion in 2024 to $162.7 billion by 2030, highlighting the increasing importance of automation. This growth is fueled by the demand for high-efficiency production processes and the integration of AI-driven technologies. As industries strive to improve their operations, robotic welding offers a solution that not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes the risk of human error.
Tips for those interested in boosting their skills through robotic welding classes include focusing on hands-on training. Engaging with actual equipment and simulations will provide practical insights that are essential in this field. Additionally, staying updated on the latest technological advancements, such as digital twin technology, can enhance your understanding of how automation is transforming the industry. Networking with professionals in the field can also provide valuable insights and potential job opportunities as the demand for robotic welding expertise continues to rise.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, robotic welding has emerged as a critical skill set, significantly enhancing efficiencies and output quality. According to a report by the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association (FMA), the integration of robotic welding can increase production rates by up to 30% while minimizing labor costs by as much as 20%. To thrive in this field, aspiring welders must cultivate a robust set of key skills, including programming, troubleshooting, and familiarity with welding technologies.
One vital skill is the ability to program and operate robotic welding machines, which requires understanding the intricacies of both the software and hardware involved. Proficiency in coding languages used in robotic applications plays a pivotal role. Furthermore, a study from the National Institute of Welding reveals that professionals who possess advanced troubleshooting abilities are 40% more likely to secure managerial positions within the industry. Continuous learning and adaptation to technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence integration in welding processes, also contribute significantly to career growth in this sector. Fostering these key skills not only prepares individuals for immediate job opportunities but also positions them favorably in the long-term trajectory of their careers in robotic welding.
Robotic welding has become an integral part of modern manufacturing, creating a demand for skilled technicians who can operate and maintain these sophisticated machines. Many institutions offer specialized training programs designed to equip students with the necessary skills. For instance, the Lincoln Electric Welding School provides a comprehensive curriculum that covers the fundamentals of robotic welding, including programming, operation, and troubleshooting. Their hands-on training approach enables students to gain real-world experience with industry-standard equipment.
Another notable program is offered by the Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College (WITC), which offers an advanced diploma in automated welding. This program emphasizes not just robotic welding techniques but also the integration of robotics with traditional welding processes. Students receive exposure to various welding technology and learn to adapt to different configurations, which is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape. Such training opportunities not only enhance technical skills but also significantly boost career prospects in a field that continues to grow.
Certification and accreditation in robotic welding education play a crucial role in enhancing the credibility and effectiveness of training programs. Institutions that offer accredited courses ensure that their curriculum meets industry standards, providing students with the relevant skills and knowledge necessary for a successful career in robotic welding. These certifications can significantly increase a graduate's employability, as employers often prefer candidates who have completed training from accredited programs.
Furthermore, certification programs frequently incorporate hands-on training and assessment, allowing students to gain practical experience with robotic welding technologies. This practical knowledge, combined with theoretical understanding, helps learners stand out in a competitive job market. As the demand for skilled robotic welders continues to rise across various industries, pursuing accredited training with recognized certification can be a beneficial step to not only boost individual skills but also expand career opportunities in an evolving technological landscape.
Robotic welding has become an essential component in various industries, offering numerous career opportunities for those skilled in this field. As manufacturers continue to automate their processes, the demand for workers who can operate and maintain robotic welding systems is on the rise. Individuals who invest in robotic welding training can open the door to high-paying positions in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. This specialization not only enhances job security but also positions welders as crucial players in optimizing productivity and efficiency.
Advancement in robotic welding careers often correlates with continuous learning and skill development. With technology constantly evolving, professionals who pursue additional certifications or advanced classes can stay relevant and competitive in the job market. Many companies value employees who are proactive about their professional growth, often leading to promotions and leadership roles within organizations. Furthermore, hands-on experience in advanced robotic welding techniques can also lead to opportunities in project management and technical support, further broadening career paths in this dynamic field.
| Course Name | Duration | Certification | Skills Learned | Career Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intro to Robotic Welding | 4 weeks | Certificate of Completion | Basic robotic programming, safety protocols | Robotic Operator, Entry-level Technician |
| Advanced Robotic Welding Techniques | 6 weeks | Advanced Certification | Troubleshooting, advanced programming | Robotic Technician, Welding Engineer |
| Robotics for Manufacturing | 8 weeks | Professional Certification | Integration with production, efficiency analysis | Manufacturing Manager, Systems Integrator |
| Robotic Welding Simulation Software | 2 weeks | Certificate of Proficiency | Simulation programming, design skills | Simulation Engineer, CAD Specialist |
| Robotic Welding Safety & Best Practices | 3 weeks | Safety Certification | Safety protocols, risk assessment | Safety Officer, Compliance Specialist |














