Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
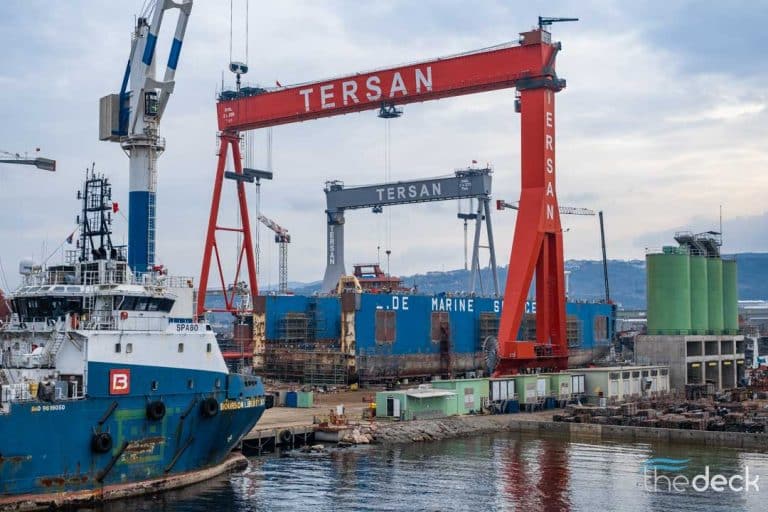

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
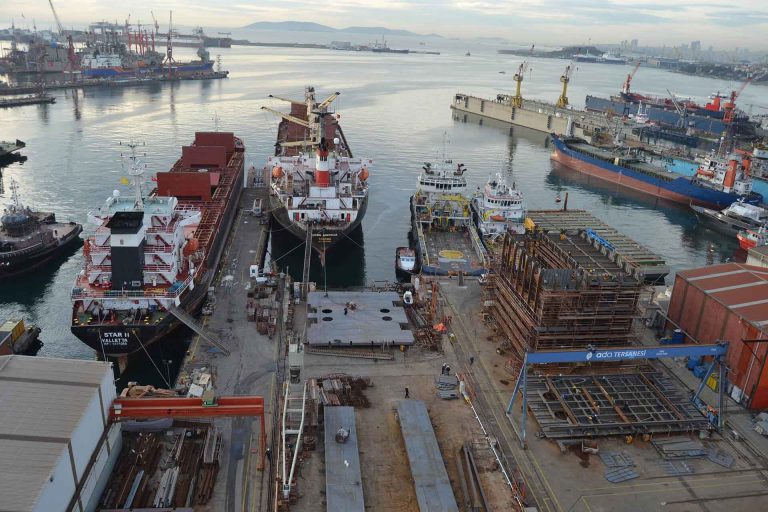

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
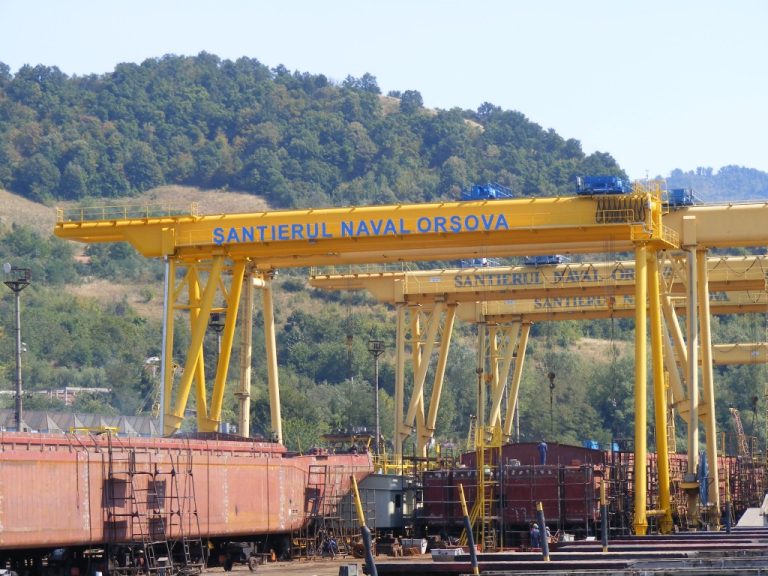

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
As the manufacturing landscape evolves, the role of the MIG welding robot is becoming increasingly significant. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the robotic welding market is expected to reach $6 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by the demand for precision and speed in welding applications. Industry expert Dr. Emily Johnson notes, “MIG welding robots are revolutionizing production lines with their efficiency and reliability.”
The advancements in MIG welding technology are remarkable. Automation enables higher weld quality and reduces human error. However, while robotic systems improve productivity, challenges remain. Many companies still struggle with integrating these intelligent machines into their existing workflows. A balance between automation and skilled labor is essential.
Despite the positive shift, companies must reflect on workforce implications. Embracing MIG welding robots doesn’t mean eliminating jobs; instead, it necessitates retraining employees for higher-skilled positions. The future is bright for MIG welding robots, but the transition requires careful consideration. It's a journey we're all part of, navigating through innovation challenges and opportunities.

The year 2026 promises exciting advancements in MIG welding robot design and functionality. One key innovation is the integration of advanced sensors. These sensors enhance the robots' ability to detect and adjust to changes in material thickness and position. This adaptability is crucial for achieving precise welds.
Increased automation is another significant trend. Many robotic systems now feature machine learning capabilities. This allows them to improve over time, learning from past welding tasks. However, this evolution brings challenges. Not all systems are equally capable of generic tasks. Some may struggle with complex geometries or specific materials.
User interfaces are also becoming more intuitive. Operators can easily program and monitor robots through simplified software. Yet, there's a learning curve. Some users may find the transition daunting. This highlights the need for ongoing training. Overall, while the technology is advancing, the importance of skilled human oversight remains clear.
The integration of AI in MIG welding robots is revolutionizing the industry. AI enhances the precision of welding, reducing errors and improving the quality of the finished product. A recent report from a leading industry research group indicated that companies implementing AI-driven technologies saw a 30% increase in weld accuracy.
These advancements do not come without challenges. For instance, the complexity of integrating AI can lead to unexpected downtime in production. Some operators find it difficult to adapt to these advanced systems. Training employees to work alongside intelligent machines is crucial but often overlooked. A study revealed that companies investing in training reported a 20% increase in overall efficiency.
Moreover, while AI can optimize welding processes, reliance on automation may create skills gaps in the workforce. Many human operators fear that their roles could become obsolete. However, skilled labor is still essential, especially for quality control and troubleshooting. Balancing automation with human expertise is necessary for long-term success in the welding industry.
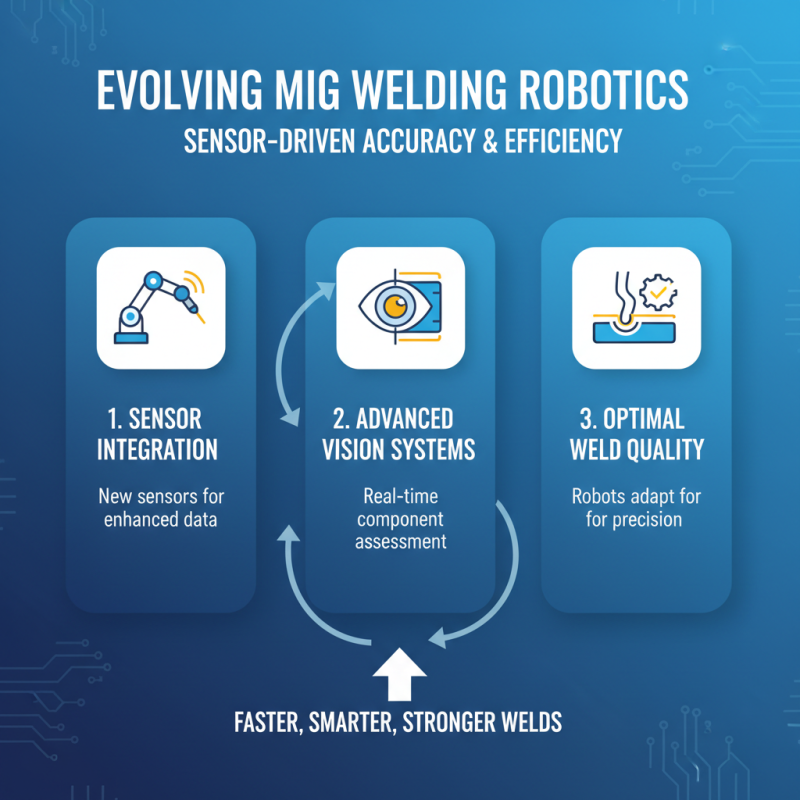
The landscape of MIG welding robot technology is evolving rapidly. Emerging sensors are at the forefront of this transformation. They enhance accuracy and efficiency in welding tasks. For instance, advanced vision systems enable robots to assess component alignment in real-time. This ensures the welder applies optimal bead geometry, improving overall weld quality.
However, challenges persist. Sensors can be costly. Implementing them may not always yield immediate gains. Additionally, calibration issues often arise, leading to inconsistencies. Researchers are addressing these problems, seeking solutions that balance innovation with practicality. Automation plays a critical role too. Integration of AI algorithms allows for better decision-making during the welding process, yet the complexity can be daunting.
The future is promising but complex. While technology advances, user expertise must also grow. Workers need training to adapt to new systems. The intersection of human skill and robotic precision is crucial. This synergy may unlock even greater potential in MIG welding applications.
The rise of Industry 4.0 significantly reshapes MIG welding robotics. Smart factories leverage data and automation, enhancing efficiency. Connected sensors gather real-time data, improving precision in welding processes. These innovations reduce errors but also introduce new challenges for operators.
Robot technology in MIG welding focuses on adaptability. Robots need to handle varying materials and weld types. Significant improvements lie in their programming. Operators face a steep learning curve with advanced software interfaces. It's essential to balance automation with human expertise.
Tips: Stay updated on the latest welding software. Regular training can help workers adapt. Embrace the learning process, as it’s crucial for success in this evolving field. Understanding the limitations of robotic systems is key. Not every situation can be resolved with automation alone.
This chart displays the key innovations in MIG welding robot technology influenced by Industry 4.0, showcasing their projected impact over the years.
MIG welding robots are becoming more sustainable. Manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly materials and processes. This shift reduces waste and energy consumption. A focus on recyclability is gaining momentum. Some manufacturers are even using renewable energy sources for power.
Water-based paints are replacing harmful solvents in production. This leads to a safer work environment. However, achieving complete sustainability is challenging. There are still hurdles to overcome, such as the disposal of old equipment. Robotic systems often contain non-recyclable parts. This issue requires urgent attention.
Continuous improvement in manufacturing practices is essential. Implementing better waste management strategies is critical. Utilizing data analytics can optimize processes further. This ensures that innovations are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible. The journey toward true sustainability in MIG welding technology is ongoing. It’s a complex path, but progress is being made.
| Innovation | Sustainability Initiative | Impact on Efficiency | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Based Welding Optimization | Reduction of Energy Consumption | Improves weld quality and speed | Lowers carbon footprint by 20% |
| Modular Robot Design | Enhancing Product Lifecycle | Facilitates upgrades and repairs | Reduces waste by 30% |
| Smart Sensor Integration | Real-time Process Monitoring | Increases uptime by 15% | Minimizes material waste |
| Eco-Friendly Filler Materials | Sourcing Sustainable Materials | Maintains integrity while reducing costs | Decreases toxicity in emissions |
| Remote Monitoring Systems | Supporting Remote Work | Enables 24/7 operation without staffing | Reduced travel emissions for staff |